Introduction: Hydroxyurea (HU) is the most used cytoreductive therapy (tx) for patients (pts) with polycythemia vera (PV). However, many pts may have suboptimal responses (SubOR) and/or toxicity (TOX) to HU. After HU, Ruxolitinib (RUX) may achieve hematocrit (HCT) and spleen reductions, but other tx are also available, mainly busulfan (BUS) and interferons (IFN).
Aims: In a large cohort of PV pts, we investigated if: 1) type of SubOR to HU influenced subsequent tx strategy; 2) differential tx had an impact on overall survival (OS).
Methods: After IRB approval, clinical/laboratory data of 2016 WHO-defined PV pts from 21 European Hematology Centers were retrospectively collected. SubOR included ≥1 of the following criteria after ≥3 mos of HU: WBC/PLT count >10/400 x109/l, need for phlebotomies (PHL); splenomegaly and/or symptoms persistence/occurrence (Barosi G et al, Blood 2009). Only pts with stable SubOR were included in this analysis. Since a complete response was never achieved, the index date (ID) was set at 3 mos from HU start in all pts (Barosi G et al, BJH 2009). OS was calculated from the ID by Cox analysis with age>80, adjusted with left truncation from PV diagnosis.
Results: At data cut-off date (June 2020), 808 PV pts were collected; 688 received HU. Among the 452 (65.7%) pts who presented a stable SubOR to HU, 41 did not receive any tx for PV due to early death or progression to BP/MF and were excluded from this analysis.
Baseline characteristics of the 411 evaluable pts were: median age: 65 yrs (21- 87); males: 54%; median (range) WBC/PLT count, x109/l: 10 (1.1-38)/465 (139-1209); median Hb (g/dl)/HCT (%): 18.6/56 (males); 17.6/54 (females); palpable splenomegaly: 38%; symptoms: 80.5%; pruritus: 42%. A previous thrombosis occurred in 104 (25.3%) pts. At least one cardiovascular risk factor (CVRF: smoke, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia and overweight) was present in 325 pts (79.1%).
After a median follow-up of 4.8 yrs (0.5-27.6) from HU start, 104 (25.3%) switched to RUX (HU-RUX), 18 (4.4%) switched to another agent (HU-other, including IFN, BUS, PHL only), and 289 (70.3%) continued HU (HU-alone).
Pts with baseline palpable spleen (p<0.001) and pruritus (p=0.01) more frequently switched to RUX. Conversely, pts ≥80y more frequently received HU-alone/other (p=0.03). Notably, Charlson Comorbidity Index and CVRF had no impact on tx strategy. Median HU daily dose was 0.65 g (≥2 g/d: 8.7% of pts) and was higher in HU-RUX pts (1 vs 0.6 g/d in HU-alone/other pts, p=0.004).
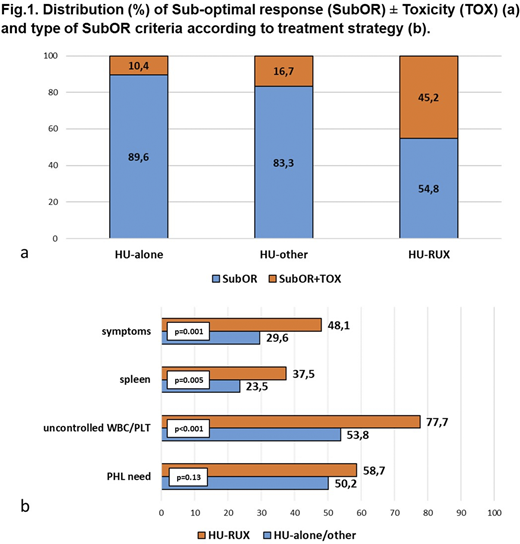
While 331 (80.5%) pts had a stable SubOR without TOX, 80 (19.5%) had also TOX. Notably, pts with only SubOR more frequently continued HU (p<0.001). Conversely, the co-occurrence of TOX was significantly associated to RUX switch (p<0.001) (Fig. 1a).
In 45.5% of pts, the SubOR was related only to uncontrolled WBC/PLT/HCT, while 16.1% of pts had an optimal hematological control but presented spleen/symptoms; the remaining 38.4% of pts had both uncontrolled myeloproliferation and spleen/symptoms. The presence of both uncontrolled myeloproliferation and spleen/symptoms significantly predicted RUX switch (p<0.001).
Investigating the SubOR criteria individually among the HU-alone/other and the HU-RUX groups, we found that uncontrolled leukocytosis and/or thrombocytosis (p<0.001), rather than PHL need (p=0.13), was significantly associated with RUX switch. Moreover, the persistence/occurrence of symptoms (p=0.001) or splenomegaly (p=0.005) were significantly associated with RUX use (Fig. 1b).
After the ID, 31 pts died. HU-RUX pts presented increased OS compared to HU-alone/other pts (p=0.03).
Conclusions. This study revealed a high rate of SubOR to HU, possibly also affected by low HU doses, and a lack of urgency to change the tx in these pts, with >70% of pts continuing HU despite the stable SubOR. Particularly, good tolerance to HU, absence of splenomegaly and pruritus, and older age were the main factors against a tx change. Notably, despite HCT>45% is associated with worse outcome (Marchioli R, NEJM 2013), PHL need did not significantly trigger tx change. The better OS in the HU-RUX group is presumably multifactorial and requires further confirmation. Overall, this analysis points out the need to improve HU management and response evaluations, weighing appropriate tx strategies in case of SubOR.
Palandri:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Benevolo:Amgen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Breccia:Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Cavazzini:Pfize: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria. Heidel:Celgene: Consultancy; CTI: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Crugnola:BMS: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Pane:Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses; Janssen: Other: Travel Expenses; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: travel expenses, Speakers Bureau; Novartis pharma SAS: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses, Speakers Bureau. Cuneo:Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Krampera:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Semenzato:Takeda: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria. Lemoli:Jazz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; BerGenBio ASA: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cavo:Jannsen, BMS, Celgene, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, Amgen, Oncopeptides, AbbVie, Karyopharm, Adaptive: Consultancy, Honoraria. Palumbo:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.